FRCR Guide
- Home
- FRCR
FRCR Examination Guide / FRCR eligibility criteria / FRCR exam structure
FRCR or Fellowship of the Royal College of Radiologists is a radiology examination which is conducted by the Royal College of Radiologists (RCR), UK.
It consists of 3 steps after which a successful candidate in inducted as a Fellow of the Royal College of Radiologists. Following this, the candidate is entitled to use the designation FRCR.
In order to work as a consultant radiologist in the UK, a successful FRCR candidate is required to register with the General Medical Council (GMC) specialty register for clinical radiology.

Am I eligible for the FRCR radiology exam?
(FRCR eligibility criteria)
First FRCR (FRCR Part 1 anatomy & Physics)
A candidate is required to be a radiology resident i.e. undergoing clinical radiology training at the time of application. However, there is no minimum training criteria for FRCR part 1 eligibility. RCR (Royal College of Radiologists) does not require you to submit any proof of this training during the application process for FRCR Part 1. However, keep your passport and photo handy at the time of application.
If you are doing your radiology training in the United Kingdom, then you have to get the approval letter of the Training Programme Director before applying for the exam.
Final FRCR Part A (FRCR 2A)
After you have passed both FRCR Part 1 Anatomy & Physics, you can apply for FRCR 2B once you have completed atleast 24 months of radiology training.
Final FRCR Part B (FRCR 2B)
After passing FRCR 2A and completing atleast 34 months of training in your radiology department, you can apply for FRCR 2B.
WHAT IS THE STRUCTURE OF THE EXAMS?
1. FIRST FRCR exam (FRCR Part 1)
First FRCR examination consists of 2 modules, namely FRCR Anatomy & FRCR Physics. These exams are usually held over a 2-day period, thrice a year – March, June and September.
FRCR exams are held in multiple locations worldwide, namely United Kingdom (London, Glasgow, Belfast, Birmingham along with Manchester for Physics and Stockport for Anatomy), Hong Kong, Cairo (Egypt), Hyderabad (India) and Singapore.
A. FRCR Anatomy:
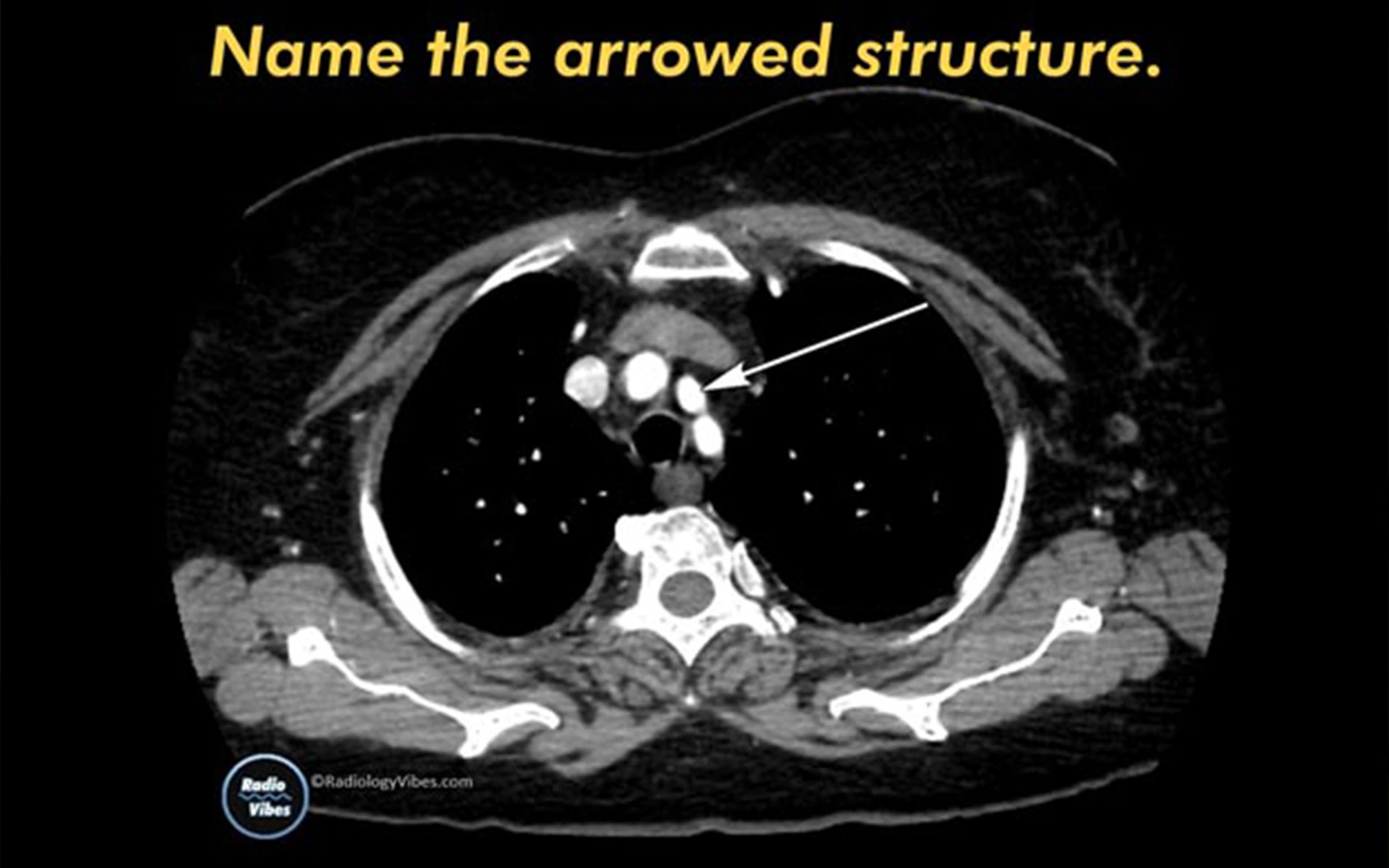
FRCR anatomy is an image-based exam held on a Viewing Workstation. The module intends to test the candidate’s grasp & basic knowledge of radiological anatomy. Current FRCR Anatomy exam format consists of 100 image based radiological anatomy questions, each question carrying 2 marks. Hence the total marks are 200.There is no negative marking. The exam time duration is 90 minutes. The passing cutoff for FRCR Anatomy exam ranges from 115 to 160, depending on the difficulty of the exam and the performance of the candidate cohort.
A precise answer to this question would be: Left Common Carotid Artery.
How do the examiners mark the anatomy answers?
The marking system for Anatomy examination is as follows:
- 0 – incorrect answer
- 1 – partially correct/less accurate answer, for example, TIBIA instead of RIGHT TIBIAL DIAPHYSIS.
- 2 – complete/accurate answer
The digital platform used by FRCR for FRCR Part 1 anatomy and FRCR 2B exams is demonstrated here by the Royal College of Radiologists.
B. FRCR Physics:
This is a multiple-choice written question (MCQ) type exam. It consists of 40 questions/topics with each question comprising 5 multiple choice statements, giving a total of 200 statements. The candidate is required to determine and answer each statement as True or False. Each statement carries 1 mark, and hence the total marks is 200. The exam time duration is 90 minutes. There is no negative marking so all questions should be attempted. The passing cutoff for Physics examination is usually around 150 (out of 200).
The syllabus for FRCR Physics paper is as follows:
- Basic Physics
- Radiography + Fluoroscopy.
- Nuclear Imaging.
- Radiation Safety
- Computed Tomography Physics
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Physics
- Ultrasonography Physics
An example of a typical physics question is as follows:
Q1. Regarding Production of X-rays... (answer as TRUE/FALSE)
- X-rays production occurs when show-moving electron blocked by Tungsten target.
- Total kinetic energy ( K.E ) of electrons is converted only into X-rays.
- Tube voltage is applied across the X-ray tube to accelerate the electrons towards the positive anode.
- Thermionic emission is the process by which an electrode emits X-Rays after acquiring thermal energy.
- The X-Rays spectrum consists of a range of energies.
Once you have passed both Anatomy & Physics modules you are considered as having passed FRCR Part 1. The maximum number of attempts at any FRCR examination is 6 (six).
2. FRCR Final Part A (FRCR 2A)
The FRCR 2A exam tests the candidate in Systemic radiology, which is divided in the following systems:
- Musculoskeletal System & Trauma
- Gastro-intestinal System
- Genito-urinary System, Obstetrics & Gynecology and breast
- Cardiothoracic and Vascular System
- Pediatrics
- Central Nervous System and Head & Neck
The Final FRCR Part A (FRCR 2A) examination consists of single best answer (SBA) type questions. The examination is divided into two separate papers held on the same exam day.
FRCR 2A Exam dates and venues (When and where is the FRCR 2A Exam held?)
The examination is held twice a year: usually in the months of June and December. The examination venues are UK (Belfast, Bristol, Birmingham, Edinburgh, Manchester and London), Hong Kong, Cairo (Egypt), Hyderabad (India) and Singapore.
Exam Pattern: Each of the 2 exam papers consist of 120 questions with each question comprising 5 multiple choice options. The candidate is required to determine the most appropriate single answer (Single best answers or SBAs) to the given question. Hence only one answer is correct. Each of the two papers is 3 hours (180 minutes) in duration. There is 1 mark for each correct answer and 0 marks for a wrong answer. There is no negative marking. Hence candidates are encouraged to attempt all the questions. The entire exam consisting of 240 questions is considered as a single exam and the candidate’s performance is assessed as a whole. It is recommended to apply for the FRCR 2A exam just after your radiology residency (MD / DNB / DMRD exams).
A typical FRCR 2A question is as follows:
A 36 year old male presented with recurrent headache and ataxia. CT Brain demonstrated a solid-cystic mass in the left cerebellar hemisphere. Subsequent MRI Showed a cystic mass with a vividly enhancing mural nodule. Abdominal ultrasonography revealed pancreatic cysts and a renal angiomyolipoma. The most likely diagnosis is:
- Pilocytic astrosytoma
- Ependymoma
- Medulloblastoma
- Gimangioblastoma
- Glioblastoma multiforme
After passing the FRCR 2A exam, you are eligible for the FRCR 2B exam (if you have completed atleast 34 months of radiology training in your department).
3. FRCR Final Part B (FRCR 2B)
All candidates who have passed the FRCR 2a (CR2A) and have completed atleast 34 months of radiological training are eligible for FRCR 2B examination. However, UK trainees and doctors already working in the NHS (NHS contributors) are given preference.
The FRCR 2B examination consists of 3 components – Rapid reporting (RR), Reporting session and Oral examination/Viva. All components are viewed on a dedicated image viewing station, similar to the one used for FRCR Anatomy examination. The written components (Rapid reporting (RR) and Reporting session) are held on a single day whereas the Oral examination/Viva is usually held after 3-7 days.
The written components (Rapid reporting (RR) and Reporting session) are held at one of the 5 UK venues - Belfast, Glasgow, Birmingham, Stockport & London and 2 new venues - Cairo (Egypt) & Hyderabad (India).
A. Rapid Reporting (RR)
The rapid reporting component consists of 30 images to be reviewed within 35 minutes. Each image carries 1 mark, so a total of 30 marks. These images are mostly plain X-rays you would report in the Emergency Department in your day to day practice. Around 10-15 of these images are usually normal. For each image, you have to write whether the Xray/scan is normal or abnormal. If abnormal, you have to state the precise abnormality. The anatomical variants are considered and marked as normal.
B. Reporting session
Reporting session (also known as Long cases) is a written component consisting of 6 cases. Each of the 6 cases usually contain two or more modalities (for example Xray, CT, MRI, USG or nuclear imaging). You have 55 minutes to complete this session and to report all findings along with the diagnosis & differentials. This carries a total of 48 marks.
C. Oral examination/Viva
This component is divided into 2 viva voce oral examinations, usually held in two different rooms. Each of these viva is conducted by 2 examiners. The examiners take turns to show you radiological cases and subsequently ask relevant questions. Each viva duration is around 30 minutes (15 minutes each per examiner). Thus, the total duration for FRCR 2B oral examination is 60 minutes.
The digital platform used by FRCR for FRCR Part 1 anatomy and FRCR 2B exams is demonstrated here by the Royal College of Radiologists:
Singapore FRCR 2B/MMed examination:
You can alternatively apply for the FRCR 2B examination in Singapore. National University of Singapore conducts a joint FRCR 2B/MMed exam every year at Singapore venue. If successful, you get the MMed degree along with the FRCR certification. However, there is an additional fee for applying for the joint Singapore FRCR 2B/MMed examination.
Details about the dates and application can be found here.
FRCR Books
Best books for FRCR
FRCR Application
How to apply for FRCR
Anatomy Mock
FRCR Anatomy Mock Exams
FRCR Strategy
FRCR Preparation strategy
FRCR Anatomy Tips
Top 10 tips for FRCR Anatomy
FRCR Results
FRCR Exam results and pass rates
FRCR Groups
Social media learning groups
FRCR FAQs
Frequently asked questions
Copyright © 2022 radiologyvibes.com | All Rights Reserved. | Developed by : Teckat.com

